Address
Room 2301C, 23rd Floor, Building 1, jinghu Commercial center, No, 34, Liangzhuang Street, Eri District, Zhengzhou City, Henan province
Woours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
Room 2301C, 23rd Floor, Building 1, jinghu Commercial center, No, 34, Liangzhuang Street, Eri District, Zhengzhou City, Henan province
Woours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

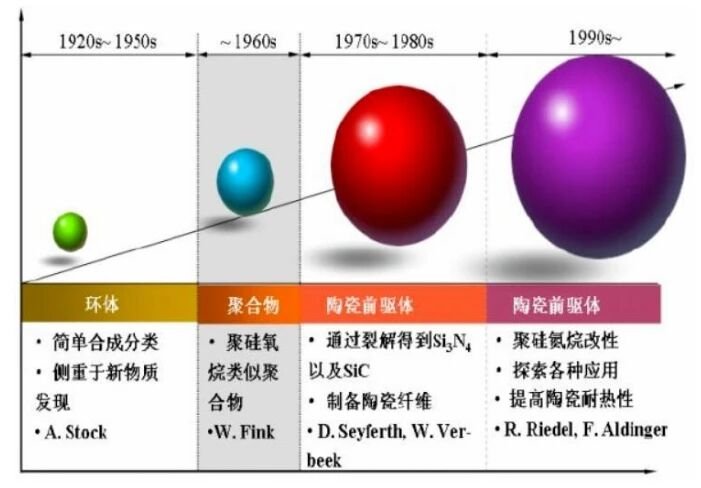
In recent years, polysilazanes, as a new type of coating, have gradually expanded from military applications to civilian production, playing an increasingly important role in the coatings industry. Polysilazanes are a class of polymers with Si-N bonds as repeating units in the backbone. Research on polysilazanes has been ongoing for nearly a century, since A. Stock et al. first reported the preparation of polysilazanes by ammonia decomposition of chlorosilanes in 1921. However, due to the complex preparation process, commercial development did not begin until the 1950s.
Polysilazane resins are among the few inorganic polymers that can cure at room temperature or heat to form high-performance membrane materials. After curing, they can achieve a hardness exceeding 9 hours and exhibit resistance to wear, corrosion, high temperature, oxidation, water, and radiation. They are primarily classified into two categories: inorganic polysilazanes (PHPS) and organic polysilazanes (OPSZ).
What is the market development of polysilazane? What is its regional distribution? What are the obstacles to market development? What are the market segments? Let’s take a look.
What is polysilazane?
Polysilazanes (PSZ) are a class of inorganic polymers with Si-N bonds as repeating units in their backbones, exhibiting unique structures and properties. Currently, mainstream polysilazane products include polysilazane coatings, polysilazane sealing materials, polysilazane composites, polysilazane sealants, and polysilazane plastics. These materials exhibit excellent insulation properties, high-temperature resistance, and chemical stability, and are widely used in semiconductors, optoelectronics, aerospace, and other fields.
Advantages of organopolysilazanes as coatings
It adheres tightly to substrates such as metal, glass, minerals, ceramics, and organic materials.
Distinctive physical properties include high hardness (9H+), UV transparency, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and thermal stability.
It provides an excellent film-forming coating suitable for use in diverse environments, with high-temperature resistance, excellent weather resistance, and excellent chemical resistance.
Industrial Chain
Raw Material Supply
The main raw materials for polysilazane are silicon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Silicon and nitrogen are key raw materials for the production of polysilazane. Silicon and nitrogen are primarily supplied by mineral resources and chemical raw materials, such as silica and ammonia.
Preparation Technology
Polysilazane preparation techniques primarily include chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and other methods. CVD involves decomposing a gaseous precursor at high temperature and depositing it onto a substrate, resulting in the production of high-quality polysilazane films.
Application Areas
Polysilazane’s downstream applications include manufacturers and R&D institutions in fields such as semiconductors, optoelectronics, and aerospace. Currently, coating materials and resin materials are the primary applications for polysilazane. Polysilazane can be converted into ceramic materials through high-temperature pyrolysis and is an important ceramic precursor. With the rapid development of the new materials industry and the growing demand for ceramic-based materials, its market potential continues to expand. Currently, the main applications of polysilazane include:
Silicon nitride, silicon boron carbon nitride and other ceramic fiber precursors
High-temperature resistant coatings
High-temperature corrosion protection for metals
Adhesives for ultra-precision ceramic parts
High-temperature resistant composite material modification
Photoresist adhesion enhancers
Lithium battery electrolyte additives
Carbon fiber anti-oxidation and high-temperature resistant coatings
Anti-graffiti coatings for transportation vehicles and buildings
Ceramic non-stick coatings for kitchenware
Self-cleaning coatings for photovoltaic cells
Non-combustible composite materials
Positive factors affecting development
High Market Demand
Polysilane (polynitrogen silane) is a new, cutting-edge material. Ceramics prepared using polysilane as a precursor exhibit properties such as ultra-high temperature resistance, ultra-toughness, ultra-thinness, ultra-corrosion resistance, and ultra-high strength. In recent years, with the advancement of industrial technology, the global market demand for ceramic-based materials has continued to increase, driving the demand for polysilane (polynitrogen silane).
National Policy Support
Polysilazane preparation technology is difficult, and foreign companies have a monopoly on the market. In recent years, to break this monopoly and fill the gap in the domestic market, Chinese companies have conducted research on polysilazane technology and applications, achieving considerable success. For example, ZhengZhou Quartz Master New Materials Co., Ltd. has successfully launched polysilazane functional coatings.
Unfavorable factors affecting development
High Costs
Overall, raw material prices fluctuate, increasing industry cost uncertainty and sometimes even causing costs to remain high. At the same time, rising labor costs place a greater burden on manufacturers.
Preparation technology is difficult
Currently, the global production of polysilazane still faces technical bottlenecks. Furthermore, polysilazane’s relatively reactive properties make storage and transportation difficult. Consequently, the polysilazane market is relatively small compared to similar polymers like polysiloxane.
Patents hinder my country’s overall competitiveness in polysilazane, which lags significantly behind developed countries. The excellent processing and product properties of polysilazane coatings offer broad application prospects. my country’s overall strength in polysilazane preparation is relatively weak. However, applicants from developed countries such as AZ Electronic Materials, Samsung Corporation, Konica Minolta Co., Ltd., and Lintec Co., Ltd. established a strong patent portfolio in my country for polysilazane coating applications early on and hold a large number of patents.
Compared to international research on polysilazane coatings, domestic research reports are relatively limited, and research on the application of polysilazane in the optoelectronics field is even rarer. This undoubtedly poses a challenge to the development of my country’s polysilazane industry. my country should strengthen research on polysilazane preparation and application methods, overcome existing difficulties, and strengthen intellectual property protection to build a competitive polysilazane coating industry chain.