Address
Room 2301C, 23rd Floor, Building 1, jinghu Commercial center, No, 34, Liangzhuang Street, Eri District, Zhengzhou City, Henan province
Woours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
Room 2301C, 23rd Floor, Building 1, jinghu Commercial center, No, 34, Liangzhuang Street, Eri District, Zhengzhou City, Henan province
Woours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

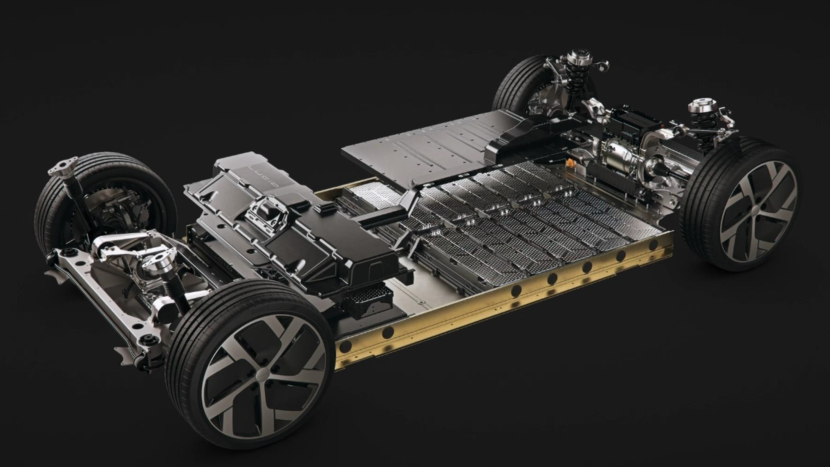
The automotive chassis, supporting the vehicle’s overall structure and numerous components from various systems, is crucial for ensuring proper operation. During daily use, the chassis inevitably endures harsh conditions such as vibration, corrosion, bumps, flying rocks, splashing water, and temperature and humidity fluctuations.
Proper chassis coating protection is not only crucial for protecting automotive components and extending their service life, but also directly contributes to the safety and comfort of drivers and passengers.
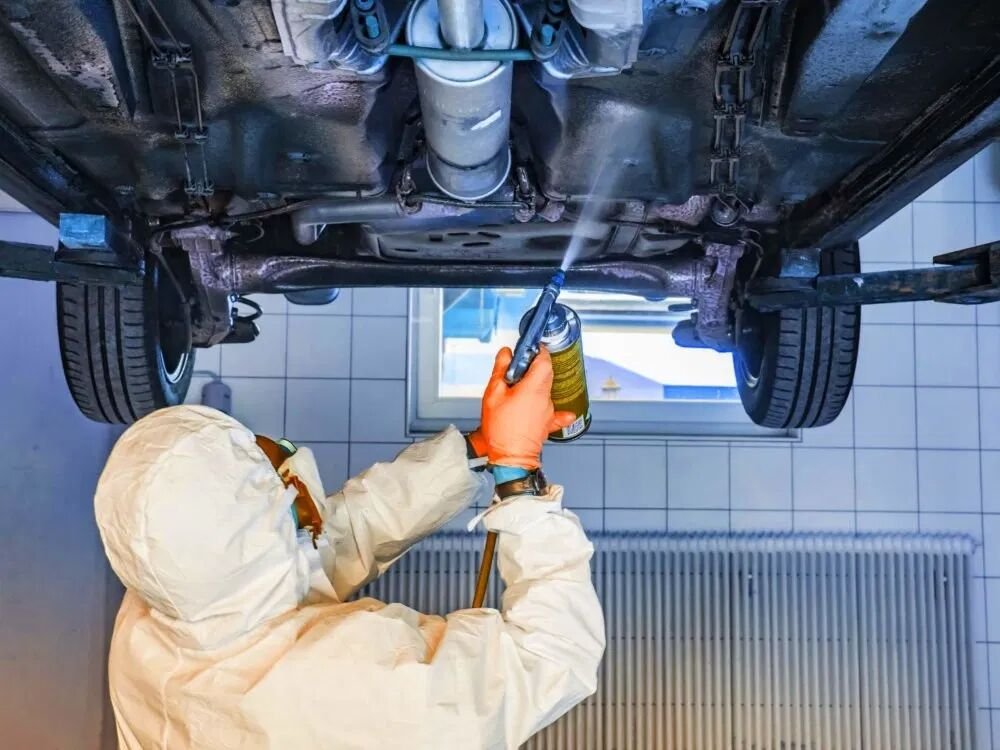
1.Stone impact resistance
As a car speeds, flying road debris can easily strike the chassis. On uneven roads, the chassis also risks colliding with hard objects, threatening the safety and lifespan of the vehicle body and components. In the era of new energy vehicles, power batteries occupy a significant portion of the chassis. Batteries are inherently fragile when struck by rocks, making the anti-stone impact performance of chassis coatings particularly important.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) anti-stone chip coating is a mainstream chassis anti-stone chip coating on the market. Introduced to the Chinese market by Volkswagen in the 1980s, it quickly gained market share in China thanks to its excellent mechanical properties, easy application, process compatibility, and low cost.
In addition to standard PVC anti-stone chip coatings, researchers have also developed low-density and foam-type anti-stone chip coatings to meet the lightweighting and functionalization needs of automobiles.
The former is made by adding a certain proportion of hollow, thin-walled, uniformly sized, and highly compressive spherical glass microspheres to the standard coating, blending and curing them. The density can be as low as 1.0 g/mL, resulting in a weight reduction of over 30% compared to standard coatings. Currently, it is primarily used in foreign and joint venture brand vehicles, and is gradually being adopted by domestic OEMs.
The latter is to add plastic foaming agent to ordinary paint, which produces gas when heated, causing the volume of the baked and cured paint to expand and become a loose and porous honeycomb structure; the foamed anti-stone chip paint has good compression resilience and good buffering and energy absorption effect when subjected to local impact, and is mainly used in Japanese models.
2.Flame retardancy and fire resistance
Spontaneous vehicle combustion accidents occur frequently due to factors such as high temperatures, oil leaks, and electrical circuit failures. Furthermore, with the rapid development of new energy vehicles, spontaneous combustion accidents caused by thermal runaway of power batteries are also common. The chassis is a densely populated area for oil and electrical circuits, and most new energy vehicles also place their power batteries within the chassis. Therefore, the flame retardancy and fire resistance of chassis coatings require special attention.
Compared to traditional solvent-based chassis coatings, water-based chassis coatings, which are dispersed using water-based resins and water as carriers, offer inherent flame retardancy. However, this is still far from sufficient for fire protection. Considering the raw materials and practical conditions of power batteries, thermal runaway can reach temperatures exceeding 1200°C, rapidly melting metal components or igniting the battery pack’s exterior coating, instantly spreading the fire throughout the chassis and even the entire vehicle.
This necessitates the addition of fire-resistant and high-temperature resistant flame retardants to chassis coatings. For example, adding an appropriate amount of zinc oxide not only improves the coating’s fire resistance but also imparts excellent corrosion resistance. Flame retardants are also essential. High-quality flame retardants such as aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide can suppress flames.
The use of fire retardants and flame retardants can elevate chassis coatings from simply being flame-retardant to being fire-resistant, effectively ensuring vehicle safety in extreme conditions and providing a safe driving experience for users.

3.Adhesion
A key performance characteristic of coatings is sufficient adhesion after film formation. Essentially, the chassis is a metal structure, and the coating used is a type of metal protective coating. However, unlike typical metal protective coatings, it operates in a dynamic environment and must withstand years of vibration, friction, and other harsh conditions, requiring strong adhesion.
To improve chassis coating adhesion, researchers have been diligently pursuing improved coating formulations. For example, some researchers have proposed using nano-calcium carbonate as a filler in PVC chassis coatings. This not only enhances the coating’s hardness and adhesion, but also improves its thixotropy and leveling properties. Studies have shown that nano-particles can expand the interaction area between the substrate and the coating, and because their surface atoms are highly activated, they promote adhesion between the coating and the substrate, making the coating stronger and more durable.
Adhesion can also be improved by optimizing the application process. For one thing, the chassis can undergo appropriate pre-treatment methods such as degreasing, phosphating, chromating, sandblasting, and polishing to remove surface grease and other contaminants and enhance the bond between the subsequent coating and the chassis substrate.
On the other hand, specific curing methods are required for different chassis components. For example, components operating in low-temperature environments are more suitable for air-drying or low-temperature baking coatings. For applications requiring a higher level of protection, the baking temperature can be increased to accelerate the cross-linking reaction, thereby achieving better adhesion.
4.Other performance
In addition to the aforementioned properties, numerous other key considerations during the R&D and production of automotive chassis coatings include sound insulation, shock absorption, corrosion resistance, weather resistance, elasticity and flexibility, environmental friendliness, and ease of application.
These properties not only ensure safety, longevity, and comfort during vehicle use, but also ensure a more efficient, high-quality, and environmentally friendly manufacturing process, complying with national and industry quality management requirements.